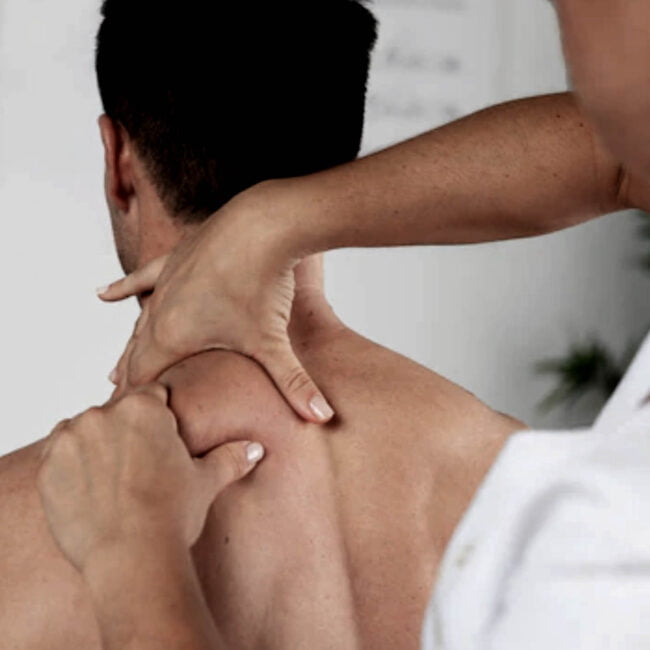
Our areas of expertise / Services
Our approach to physiotherapy is holistic, where we take into account your physical, emotional, and lifestyle factors when developing a treatment plan. We use evidence-based techniques and the latest technology to deliver the most effective and most efficient care. Experience top-notch physiotherapy services in Mississauga and regain your mobility. Explore our services to Book a Session, Take the first step towards a healthier, stronger you!.
FAQs
Absolutely. Our physiotherapists are highly trained, licensed professionals with extensive experience in the field. They are dedicated to providing personalized care and staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in physiotherapy techniques and treatments.
Many insurance plans cover some or all of the costs associated with physiotherapy sessions. It is important to check with your insurance provider to understand your coverage and any specific requirements they may have, such as a doctor’s referral.
- We have a team of multidisciplinary practitioners who use hands-on manual therapy techniques to treat various conditions and injuries.
- We have a registered physiotherapist who is certified and licensed and recognized as one of the top 3 practitioners in the Mississauga area.
- Curezone provide personalized and effective treatments that are based on evidence and best practices.
- We offer a range of services such as laser therapy, pelvic floor physiotherapy, shock wave therapy, spinal decompression, massage therapy, acupuncture, and more.
- We have a convenient location, flexible timings, direct billing, and online booking options.
During a physiotherapy session, your therapist will assess your condition, evaluate your range of motion, strength, and flexibility, and develop a personalized treatment plan. Treatment may include manual therapy, exercises, modalities (such as heat or cold therapy), and education on self-management techniques.
Booking an appointment before coming to the clinic will help you save time. However, we also welcome urgent care cases.
ExcellentBased on 361 reviews
 Sumaya Hassen2024-04-02Since 2021, I've intermittently visited Sheena for back pain, previously experiencing discomfort when sitting. Prior to Sheena, another physiotherapist's misguided exercises worsened my condition. Sheena's treatments vastly improved my quality of life, allowing me to sit comfortably for extended periods. After a recent car accident causing whiplash and neck pain, Sheena swiftly aided my recovery. Her neck massages not only relieved longstanding headaches but also corrected my posture, addressing pain in other areas. Sheena's expertise, honesty, and encouragement have been invaluable. She's not only knowledgeable but also genuinely cares about getting her patients back on track. She consistently reminds me to do the exercises, motivating me to actively participate in my recovery. I'm immensely grateful to her and the Curezeone team who have also been great and display exceptional customer service.
Sumaya Hassen2024-04-02Since 2021, I've intermittently visited Sheena for back pain, previously experiencing discomfort when sitting. Prior to Sheena, another physiotherapist's misguided exercises worsened my condition. Sheena's treatments vastly improved my quality of life, allowing me to sit comfortably for extended periods. After a recent car accident causing whiplash and neck pain, Sheena swiftly aided my recovery. Her neck massages not only relieved longstanding headaches but also corrected my posture, addressing pain in other areas. Sheena's expertise, honesty, and encouragement have been invaluable. She's not only knowledgeable but also genuinely cares about getting her patients back on track. She consistently reminds me to do the exercises, motivating me to actively participate in my recovery. I'm immensely grateful to her and the Curezeone team who have also been great and display exceptional customer service. Megan D2024-04-01Sheena has great in-depth knowledge and workings of the body. She's a great physiotherapist and has helped me through my injuries
Megan D2024-04-01Sheena has great in-depth knowledge and workings of the body. She's a great physiotherapist and has helped me through my injuries Sandy Felizardo2024-03-28Sheena is great! Everyone is very helpful and attentive.
Sandy Felizardo2024-03-28Sheena is great! Everyone is very helpful and attentive. Mandy Louray2024-03-28Staff here is so friendly and well aware of what they are doing. I was great experience having my physio here
Mandy Louray2024-03-28Staff here is so friendly and well aware of what they are doing. I was great experience having my physio here Mark Vasquez2024-03-28Curezone relief ,revive,regain. Thanks Zeena and staff.wonderful service!
Mark Vasquez2024-03-28Curezone relief ,revive,regain. Thanks Zeena and staff.wonderful service! Alex Bennet2024-03-28I wanna shout out to Sheena and her team named Curezone Physiotherapy, it's not only the Curezone it's beyond that(there is a word in the Tamil language "athaiyum thaandi......"). My kid is 5 years old and he was unable to sit with a crisscross posture. After a few sessions, he is now able to sit crisscross for a longer time. The entire team was more welcoming to my kid. He was cozy for the whole session like how he goes to playschool. Keep growing and rockinnnnnnnn!!!!!!!!!!
Alex Bennet2024-03-28I wanna shout out to Sheena and her team named Curezone Physiotherapy, it's not only the Curezone it's beyond that(there is a word in the Tamil language "athaiyum thaandi......"). My kid is 5 years old and he was unable to sit with a crisscross posture. After a few sessions, he is now able to sit crisscross for a longer time. The entire team was more welcoming to my kid. He was cozy for the whole session like how he goes to playschool. Keep growing and rockinnnnnnnn!!!!!!!!!! Amna Al-khayaat2024-03-23Great and friendly team, Sheena is a great physiotherapist, I have been seeing so much improvement since I started my treatment. Thank you curezone team.
Amna Al-khayaat2024-03-23Great and friendly team, Sheena is a great physiotherapist, I have been seeing so much improvement since I started my treatment. Thank you curezone team. Jass Nandra2024-03-23Great service. Recommended to all. I have neck pain and only in 3 weeks i feel improvement. Ishita naik is great she helped a lot and very kindful.
Jass Nandra2024-03-23Great service. Recommended to all. I have neck pain and only in 3 weeks i feel improvement. Ishita naik is great she helped a lot and very kindful. Ira Tan2024-03-21Physiotherapists Sheena and Ishita provided excellent care after my Motor Vehicle Accident, demonstrating superb customer service. They were accommodating with scheduling, attentive during sessions, and proactive in follow-ups. Their clear communication and personalized attention made the experience comfortable and effective. I highly recommend them for their outstanding physiotherapy and top-notch customer service. Edit: Based on other reviews, I recommend highlighting the importance of openly communicating about the area, severity, and type of pain you’re experiencing, as well as any concerns you may have before, during, or after sessions.
Ira Tan2024-03-21Physiotherapists Sheena and Ishita provided excellent care after my Motor Vehicle Accident, demonstrating superb customer service. They were accommodating with scheduling, attentive during sessions, and proactive in follow-ups. Their clear communication and personalized attention made the experience comfortable and effective. I highly recommend them for their outstanding physiotherapy and top-notch customer service. Edit: Based on other reviews, I recommend highlighting the importance of openly communicating about the area, severity, and type of pain you’re experiencing, as well as any concerns you may have before, during, or after sessions. Sukhveer Kaur2024-03-20I had shoulder and back pain from almost a year. After attended few sessions my pain is improving a lot. For their wonderful care, Sheena and her staff have my deepest appreciation. I will heartily suggest it to anyone else in need of physiotherapy.
Sukhveer Kaur2024-03-20I had shoulder and back pain from almost a year. After attended few sessions my pain is improving a lot. For their wonderful care, Sheena and her staff have my deepest appreciation. I will heartily suggest it to anyone else in need of physiotherapy.